関連記事
- Part 1: 環境セットアップ
- Part 2: System call Interface
- Part 3: VFS
- Part 4: ext2 (1) write_iter
- Part 5: ext2 (2) write_begin
- Part 6: ext2 (3) get_block
- Part 7: ext2 (4) write_end
- Part 8: writeback (1) work Queue
- Part 9: writeback (2) wb_writeback
- Part 10: writeback (3) writepages
- Part 11: writeback (4) write_inode
- Part 12: block (1) submit_bio
- Part 13: block (2) blk_mq
- Part 14: I/O scheduler (1) mq-deadline
- Part 15: I/O scheduler (2) insert_request
- Part 16: I/O scheduler (3) dispatch_request
- Part 17: block (3) blk_mq_run_work_fn
- Part 18: block (4) block: blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched
- Part 19: MMC (1) initialization
- Part 20: PL181 (1) mmci_probe
- Part 21: MMC (2) mmc_start_host
- Part 22: MMC (3) mmc_rescan
概要
QEMUの vexpress-a9 (arm) で Linux 5.15を起動させながら、ファイル書き込みのカーネル処理を確認していく。
本章では、I/Oスケジューラからリクエストをディスパッチしてから、ブロックデバイスドライバにリクエストを発行する (queue_rq )までを確認した。
はじめに
ユーザプロセスはファイルシステムという機構によって記憶装置上のデータをファイルという形式で書き込み・読み込みすることができる。
本調査では、ユーザプロセスがファイルに書き込み要求を実行したときにLinuxカーネルではどのような処理が実行されるかを読み解いていく。
調査対象や環境などはPart 1: 環境セットアップを参照。
I/Oスケジューラからリクエストをディスパッチする
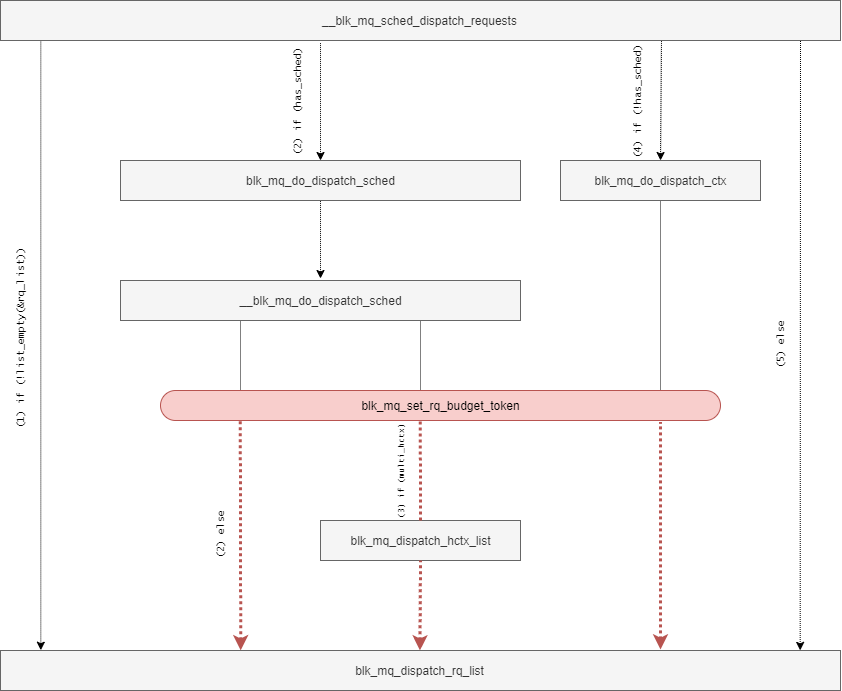
blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数は、I/Oスケジューラからリクエストをディスパッチするための関数である。
I/Oスケジューラが設定されている場合に、__blk_mq_sched_dispatch_requests関数から呼び出される。
Hardware Dispatch Queue を引数として受け取り、リクエストがディスパッチ完了したときに true を返す。
blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数の定義は次の通りとなっている。
// 209: static int blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx) { int ret; do { ret = __blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched(hctx); } while (ret == 1); return ret; }
blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数は、__blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数を呼び出すためのラッパ関数となっている。
__blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数では、さらにディスパッチが必要な場合に 1を返し(ディスパッチがまだ必要な場合には、 whileループで繰り返す)、そうではない場合に 0または -EAGAINを返す 。
__blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数の定義は次の通りとなっている。
// 118: static int __blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx) { struct request_queue *q = hctx->queue; struct elevator_queue *e = q->elevator; bool multi_hctxs = false, run_queue = false; bool dispatched = false, busy = false; unsigned int max_dispatch; LIST_HEAD(rq_list); int count = 0; if (hctx->dispatch_busy) max_dispatch = 1; else max_dispatch = hctx->queue->nr_requests; do { struct request *rq; int budget_token; if (e->type->ops.has_work && !e->type->ops.has_work(hctx)) break; if (!list_empty_careful(&hctx->dispatch)) { busy = true; break; } budget_token = blk_mq_get_dispatch_budget(q); if (budget_token < 0) break; rq = e->type->ops.dispatch_request(hctx); if (!rq) { blk_mq_put_dispatch_budget(q, budget_token); /* * We're releasing without dispatching. Holding the * budget could have blocked any "hctx"s with the * same queue and if we didn't dispatch then there's * no guarantee anyone will kick the queue. Kick it * ourselves. */ run_queue = true; break; } blk_mq_set_rq_budget_token(rq, budget_token); /* * Now this rq owns the budget which has to be released * if this rq won't be queued to driver via .queue_rq() * in blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list(). */ list_add_tail(&rq->queuelist, &rq_list); count++; if (rq->mq_hctx != hctx) multi_hctxs = true; /* * If we cannot get tag for the request, stop dequeueing * requests from the IO scheduler. We are unlikely to be able * to submit them anyway and it creates false impression for * scheduling heuristics that the device can take more IO. */ if (!blk_mq_get_driver_tag(rq)) break; } while (count < max_dispatch); if (!count) { if (run_queue) blk_mq_delay_run_hw_queues(q, BLK_MQ_BUDGET_DELAY); } else if (multi_hctxs) { /* * Requests from different hctx may be dequeued from some * schedulers, such as bfq and deadline. * * Sort the requests in the list according to their hctx, * dispatch batching requests from same hctx at a time. */ list_sort(NULL, &rq_list, sched_rq_cmp); do { dispatched |= blk_mq_dispatch_hctx_list(&rq_list); } while (!list_empty(&rq_list)); } else { dispatched = blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list(hctx, &rq_list, count); } if (busy) return -EAGAIN; return !!dispatched; }
__blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数では、二つの処理に分けることができる。
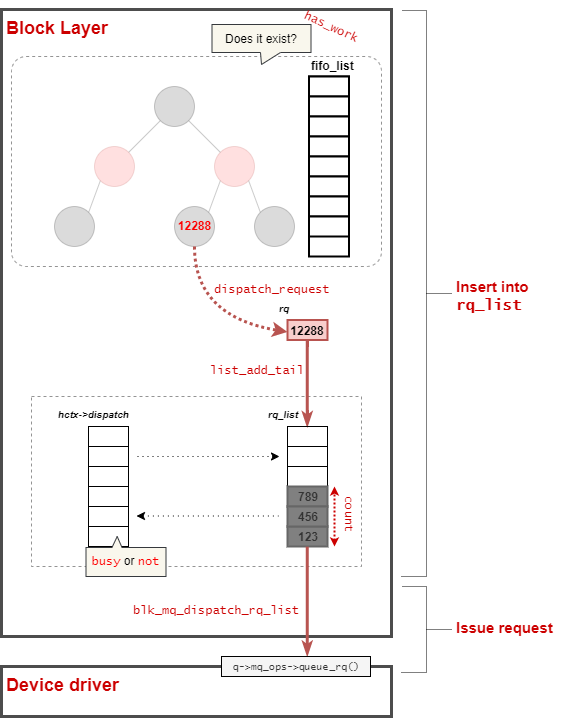
ディスパッチ候補のリクエストをキューに追加する
__blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数から該当部分を抜粋する。
// 133: do { struct request *rq; int budget_token; if (e->type->ops.has_work && !e->type->ops.has_work(hctx)) break; if (!list_empty_careful(&hctx->dispatch)) { busy = true; break; } budget_token = blk_mq_get_dispatch_budget(q); if (budget_token < 0) break; rq = e->type->ops.dispatch_request(hctx); if (!rq) { blk_mq_put_dispatch_budget(q, budget_token); /* * We're releasing without dispatching. Holding the * budget could have blocked any "hctx"s with the * same queue and if we didn't dispatch then there's * no guarantee anyone will kick the queue. Kick it * ourselves. */ run_queue = true; break; } blk_mq_set_rq_budget_token(rq, budget_token); /* * Now this rq owns the budget which has to be released * if this rq won't be queued to driver via .queue_rq() * in blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list(). */ list_add_tail(&rq->queuelist, &rq_list); count++; if (rq->mq_hctx != hctx) multi_hctxs = true; /* * If we cannot get tag for the request, stop dequeueing * requests from the IO scheduler. We are unlikely to be able * to submit them anyway and it creates false impression for * scheduling heuristics that the device can take more IO. */ if (!blk_mq_get_driver_tag(rq)) break; } while (count < max_dispatch);
ここでは、特定回数max_dispatchだけ次のような処理を実施する。
- I/Oスケジューラに対して、リクエストが存在しているか確認する
- dispatch候補リストにリクエストが存在していれば、そちらを優先する
- I/Oスケジューラに対して、ディスパッチするリクエストを取得する
- リクエストを
rq_listに追加する
max_dispatchは、基本的には キューの深さになるが、 dispatch_busy状態の場合には 1 となる。
dispatch_busyは、blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy関数によって更新される。
// 1210: static void blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx, bool busy) { unsigned int ewma; ewma = hctx->dispatch_busy; if (!ewma && !busy) return; ewma *= BLK_MQ_DISPATCH_BUSY_EWMA_WEIGHT - 1; if (busy) ewma += 1 << BLK_MQ_DISPATCH_BUSY_EWMA_FACTOR; ewma /= BLK_MQ_DISPATCH_BUSY_EWMA_WEIGHT; hctx->dispatch_busy = ewma; }
blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy関数は、blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list関数(この後に呼ばれる)と__blk_mq_issue_directly関数から呼び出される。
いずれの場合もデバイスドライバにリクエストを発行し、何かしらの理由(再実行が必要など)で拒否された場合に busy状態となり、処理が完了した場合にbusy状態が解除する。
ただし、dispatchキューにリクエストがすでに入っている場合に、I/Oスケジューラからのリクエスト抽出を中止する。
また、ブロックデバイスがSCSIを介している場合には、budgetを確認する必要がある。
リクエストキュー毎にの深さが存在しているため、I/Oスケジューラからリクエストをディスパッチする前後でget_budgetとset_budgetを呼ぶ必要がある。
ただし、mmcドライバでは上記に対応していないため、詳細は割愛する。
その後、dispatch_requestで選択したリクエストrqをrq_listに追加していく。
キューにあるリクエストをブロックレイヤーに発行する
I/Oスケジューラからディスパッチされたリクエストをrq_listに追加した後、条件によってこれらのリクエストの取り扱いが異なる。
// 185: if (!count) { if (run_queue) blk_mq_delay_run_hw_queues(q, BLK_MQ_BUDGET_DELAY); } else if (multi_hctxs) { /* * Requests from different hctx may be dequeued from some * schedulers, such as bfq and deadline. * * Sort the requests in the list according to their hctx, * dispatch batching requests from same hctx at a time. */ list_sort(NULL, &rq_list, sched_rq_cmp); do { dispatched |= blk_mq_dispatch_hctx_list(&rq_list); } while (!list_empty(&rq_list)); } else { dispatched = blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list(hctx, &rq_list, count); } if (busy) return -EAGAIN; return !!dispatched; }
I/Oスケジューラからリクエストをディスパッチできなかった場合、Dispatch用のWorkをWork Queueに追加 (BLK_MQ_BUDGET_DELAY (3ms) 後に遅延実行) される。
複数のHardware Dispatch Queueを持つ場合には同じQueueで処理する必要がある。
その場合、該当のQueueに対応するリクエストを rq_listから取り出し、blk_mq_dispatch_rq_listを呼び出す。
デバイスドライバにリクエストを発行する
blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list関数は、ブロックデバイスにリクエストを発行する関数である。
I/Oスケジューラが設定されている場合に、__blk_mq_sched_dispatch_requests関数から呼び出される。
Hardware Dispatch Queue (hctx) と 発行するリクエストのリスト(list)、budget完了数(nr_budgets) を引数として受け取り、リクエストがディスパッチ完了したときに true を返す。
blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list関数の定義は次の通りとなっている。
// 1319: bool blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list(struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx, struct list_head *list, unsigned int nr_budgets) { enum prep_dispatch prep; struct request_queue *q = hctx->queue; struct request *rq, *nxt; int errors, queued; blk_status_t ret = BLK_STS_OK; LIST_HEAD(zone_list); bool needs_resource = false; if (list_empty(list)) return false; /* * Now process all the entries, sending them to the driver. */ errors = queued = 0; do { struct blk_mq_queue_data bd; rq = list_first_entry(list, struct request, queuelist); WARN_ON_ONCE(hctx != rq->mq_hctx); prep = blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq(rq, !nr_budgets); if (prep != PREP_DISPATCH_OK) break; list_del_init(&rq->queuelist); bd.rq = rq; /* * Flag last if we have no more requests, or if we have more * but can't assign a driver tag to it. */ if (list_empty(list)) bd.last = true; else { nxt = list_first_entry(list, struct request, queuelist); bd.last = !blk_mq_get_driver_tag(nxt); } /* * once the request is queued to lld, no need to cover the * budget any more */ if (nr_budgets) nr_budgets--; ret = q->mq_ops->queue_rq(hctx, &bd); switch (ret) { case BLK_STS_OK: queued++; break; case BLK_STS_RESOURCE: needs_resource = true; fallthrough; case BLK_STS_DEV_RESOURCE: blk_mq_handle_dev_resource(rq, list); goto out; case BLK_STS_ZONE_RESOURCE: /* * Move the request to zone_list and keep going through * the dispatch list to find more requests the drive can * accept. */ blk_mq_handle_zone_resource(rq, &zone_list); needs_resource = true; break; default: errors++; blk_mq_end_request(rq, ret); } } while (!list_empty(list)); out: if (!list_empty(&zone_list)) list_splice_tail_init(&zone_list, list); hctx->dispatched[queued_to_index(queued)]++; /* If we didn't flush the entire list, we could have told the driver * there was more coming, but that turned out to be a lie. */ if ((!list_empty(list) || errors) && q->mq_ops->commit_rqs && queued) q->mq_ops->commit_rqs(hctx); /* * Any items that need requeuing? Stuff them into hctx->dispatch, * that is where we will continue on next queue run. */ if (!list_empty(list)) { bool needs_restart; /* For non-shared tags, the RESTART check will suffice */ bool no_tag = prep == PREP_DISPATCH_NO_TAG && (hctx->flags & BLK_MQ_F_TAG_QUEUE_SHARED); if (nr_budgets) blk_mq_release_budgets(q, list); spin_lock(&hctx->lock); list_splice_tail_init(list, &hctx->dispatch); spin_unlock(&hctx->lock); /* * Order adding requests to hctx->dispatch and checking * SCHED_RESTART flag. The pair of this smp_mb() is the one * in blk_mq_sched_restart(). Avoid restart code path to * miss the new added requests to hctx->dispatch, meantime * SCHED_RESTART is observed here. */ smp_mb(); /* * If SCHED_RESTART was set by the caller of this function and * it is no longer set that means that it was cleared by another * thread and hence that a queue rerun is needed. * * If 'no_tag' is set, that means that we failed getting * a driver tag with an I/O scheduler attached. If our dispatch * waitqueue is no longer active, ensure that we run the queue * AFTER adding our entries back to the list. * * If no I/O scheduler has been configured it is possible that * the hardware queue got stopped and restarted before requests * were pushed back onto the dispatch list. Rerun the queue to * avoid starvation. Notes: * - blk_mq_run_hw_queue() checks whether or not a queue has * been stopped before rerunning a queue. * - Some but not all block drivers stop a queue before * returning BLK_STS_RESOURCE. Two exceptions are scsi-mq * and dm-rq. * * If driver returns BLK_STS_RESOURCE and SCHED_RESTART * bit is set, run queue after a delay to avoid IO stalls * that could otherwise occur if the queue is idle. We'll do * similar if we couldn't get budget or couldn't lock a zone * and SCHED_RESTART is set. */ needs_restart = blk_mq_sched_needs_restart(hctx); if (prep == PREP_DISPATCH_NO_BUDGET) needs_resource = true; if (!needs_restart || (no_tag && list_empty_careful(&hctx->dispatch_wait.entry))) blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx, true); else if (needs_restart && needs_resource) blk_mq_delay_run_hw_queue(hctx, BLK_MQ_RESOURCE_DELAY); blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy(hctx, true); return false; } else blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy(hctx, false); return (queued + errors) != 0; }
blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list関数を次の三つの処理に分割して確認する。
リクエスト発行の前処理
// 1330: if (list_empty(list)) return false; /* * Now process all the entries, sending them to the driver. */ errors = queued = 0; do { struct blk_mq_queue_data bd; rq = list_first_entry(list, struct request, queuelist); WARN_ON_ONCE(hctx != rq->mq_hctx); prep = blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq(rq, !nr_budgets); if (prep != PREP_DISPATCH_OK) break; list_del_init(&rq->queuelist); bd.rq = rq; /* * Flag last if we have no more requests, or if we have more * but can't assign a driver tag to it. */ if (list_empty(list)) bd.last = true; else { nxt = list_first_entry(list, struct request, queuelist); bd.last = !blk_mq_get_driver_tag(nxt); } /* * once the request is queued to lld, no need to cover the * budget any more */ if (nr_budgets) nr_budgets--;
ブロックデバイスにリクエストを発行する前処理として、次のようなセットアップを実施する。
発行するリクエストのリスト(list) からリクエストを取り出していき、blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq関数によって検証していく。
blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq関数の定義は次の通りとなっている。
// 1265: static enum prep_dispatch blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq(struct request *rq, bool need_budget) { struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx = rq->mq_hctx; int budget_token = -1; if (need_budget) { budget_token = blk_mq_get_dispatch_budget(rq->q); if (budget_token < 0) { blk_mq_put_driver_tag(rq); return PREP_DISPATCH_NO_BUDGET; } blk_mq_set_rq_budget_token(rq, budget_token); } if (!blk_mq_get_driver_tag(rq)) { /* * The initial allocation attempt failed, so we need to * rerun the hardware queue when a tag is freed. The * waitqueue takes care of that. If the queue is run * before we add this entry back on the dispatch list, * we'll re-run it below. */ if (!blk_mq_mark_tag_wait(hctx, rq)) { /* * All budgets not got from this function will be put * together during handling partial dispatch */ if (need_budget) blk_mq_put_dispatch_budget(rq->q, budget_token); return PREP_DISPATCH_NO_TAG; } } return PREP_DISPATCH_OK; }
blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq関数は、「(必要であれば) debgetの取得」と「tagの割り当て」を実施する。
budgetの取得について、blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched関数経由から呼び出す場合には、blk_mq_set_rq_budget_token関数を実行しているため不要である。
ただし、特定のフローでは blk_mq_set_rq_budget_token関数が呼ばれていないため、blk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq関数で呼び出す。
ここで、budgetの確保に失敗した場合には PREP_DISPATCH_NO_BUDGETとして、以降のリクエストのdispatch処理を終了させる。
その後、blk_mq_get_driver_tag関数で tag の割り当てを実施する。
blk_mq_get_driver_tag関数では、tag の割り当てできた (すでにできている) 場合に trueを返す。
blk_mq_get_driver_tag関数の定義は次の通りとなっている。
// 1094: bool blk_mq_get_driver_tag(struct request *rq) { struct blk_mq_hw_ctx *hctx = rq->mq_hctx; if (rq->tag == BLK_MQ_NO_TAG && !__blk_mq_get_driver_tag(rq)) return false; if ((hctx->flags & BLK_MQ_F_TAG_QUEUE_SHARED) && !(rq->rq_flags & RQF_MQ_INFLIGHT)) { rq->rq_flags |= RQF_MQ_INFLIGHT; __blk_mq_inc_active_requests(hctx); } hctx->tags->rqs[rq->tag] = rq; return true; }
tag の割り当てができたリクエストは blk_mq_queue_data型でデータをラッピングして、ブロックデバイスへのリクエストに取り掛かる。
blk_mq_queue_data型は末尾かどうかを表すフラグ last を持ったリスト型となっている。
リクエスト発行の本処理
// 1368: ret = q->mq_ops->queue_rq(hctx, &bd); switch (ret) { case BLK_STS_OK: queued++; break; case BLK_STS_RESOURCE: needs_resource = true; fallthrough; case BLK_STS_DEV_RESOURCE: blk_mq_handle_dev_resource(rq, list); goto out; case BLK_STS_ZONE_RESOURCE: /* * Move the request to zone_list and keep going through * the dispatch list to find more requests the drive can * accept. */ blk_mq_handle_zone_resource(rq, &zone_list); needs_resource = true; break; default: errors++; blk_mq_end_request(rq, ret); } } while (!list_empty(list));
ブロックデバイスは専用のインターフェースが用意されており、そこで固有の操作を登録する。
ブロックデバイスへのリクエストは queue_rqによってリクエストを発行することができる。
デバイスの状態に応じて、リクエストの発行から帰ってくるステータスは大きく分けて3種類ある。
BLK_STS_OK: リクエストは正常に発行でき、デバイスドライバのキューにリクエストを追加されたBLK_STS*_RESOURCE: リソースがビジー状態となっており、デバイスドライバのキューにリクエストを追加できなかった- その他
リソースがビジー状態となっていた場合には、現在のリクエストをhctx->dispatchに追加し、 needs_resourceフラグにより 3ms後に再実行することになる。
リクエスト発行の後処理
// 1393: out: if (!list_empty(&zone_list)) list_splice_tail_init(&zone_list, list); hctx->dispatched[queued_to_index(queued)]++; /* If we didn't flush the entire list, we could have told the driver * there was more coming, but that turned out to be a lie. */ if ((!list_empty(list) || errors) && q->mq_ops->commit_rqs && queued) q->mq_ops->commit_rqs(hctx); /* * Any items that need requeuing? Stuff them into hctx->dispatch, * that is where we will continue on next queue run. */ if (!list_empty(list)) { bool needs_restart; /* For non-shared tags, the RESTART check will suffice */ bool no_tag = prep == PREP_DISPATCH_NO_TAG && (hctx->flags & BLK_MQ_F_TAG_QUEUE_SHARED); if (nr_budgets) blk_mq_release_budgets(q, list); spin_lock(&hctx->lock); list_splice_tail_init(list, &hctx->dispatch); spin_unlock(&hctx->lock); /* * Order adding requests to hctx->dispatch and checking * SCHED_RESTART flag. The pair of this smp_mb() is the one * in blk_mq_sched_restart(). Avoid restart code path to * miss the new added requests to hctx->dispatch, meantime * SCHED_RESTART is observed here. */ smp_mb(); /* * If SCHED_RESTART was set by the caller of this function and * it is no longer set that means that it was cleared by another * thread and hence that a queue rerun is needed. * * If 'no_tag' is set, that means that we failed getting * a driver tag with an I/O scheduler attached. If our dispatch * waitqueue is no longer active, ensure that we run the queue * AFTER adding our entries back to the list. * * If no I/O scheduler has been configured it is possible that * the hardware queue got stopped and restarted before requests * were pushed back onto the dispatch list. Rerun the queue to * avoid starvation. Notes: * - blk_mq_run_hw_queue() checks whether or not a queue has * been stopped before rerunning a queue. * - Some but not all block drivers stop a queue before * returning BLK_STS_RESOURCE. Two exceptions are scsi-mq * and dm-rq. * * If driver returns BLK_STS_RESOURCE and SCHED_RESTART * bit is set, run queue after a delay to avoid IO stalls * that could otherwise occur if the queue is idle. We'll do * similar if we couldn't get budget or couldn't lock a zone * and SCHED_RESTART is set. */ needs_restart = blk_mq_sched_needs_restart(hctx); if (prep == PREP_DISPATCH_NO_BUDGET) needs_resource = true; if (!needs_restart || (no_tag && list_empty_careful(&hctx->dispatch_wait.entry))) blk_mq_run_hw_queue(hctx, true); else if (needs_restart && needs_resource) blk_mq_delay_run_hw_queue(hctx, BLK_MQ_RESOURCE_DELAY); blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy(hctx, true); return false; } else blk_mq_update_dispatch_busy(hctx, false); return (queued + errors) != 0;
dispatchされたリクエストの個数は debugfsインターフェースで確認することができる。
リクエスト発行の後処理では、まず初めにこれを更新する。
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/block/mmcblk0/hctx0/dispatched
0 0
1 8
2 1
4 0
8 0
16 0
32+ 0
SCSI や NMVe といったデバイスドライバで、リクエストの最後尾を判断する必要がある。
そのようなデバイスに対して、 commit_rqsを呼び出すことでリクエストの末尾を通知する。(ただし、今回の環境でもあるSDカードに対して不要)
その後、デバイスドライバのキューにリクエストの追加に失敗した場合などに、dispatch処理の再実行を試みる。
ただし、Hardware dispatch Queueのステータス管理が複雑となっているため、気を付けるポイントが存在する。
blk-mqでは、ディスパッチの再実行が必要な場合のフラグとして BLK_MQ_S_SCHED_RESTARTが存在する。
このフラグは、PREFLUSH/FUAリクエストの完了時 (blk_mq_sched_restart関数)にフラグがセットされている場合にクリアされる。
これらは別のプロセッサで動作する可能性があるため、メモリバリアが必要になる。
memory barriers have to be used for ordering the following two pair of OPs:
1) adding requests to hctx->dispatch and checking SCHED_RESTART inblk_mq_dispatch_rq_list()
2) clearing SCHED_RESTART and checking if there is request in hctx->dispatch in blk_mq_sched_restart().Without the added memory barrier, either:
1) blk_mq_sched_restart() may miss requests added to hctx->dispatch meantime blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list() observes SCHED_RESTART, and not run queue in dispatch side
or
2) blk_mq_dispatch_rq_list still sees SCHED_RESTART, and not run queue in dispatch side, meantime checking if there is request in hctx->dispatch from blk_mq_sched_restart() is missed.
この場合、Hardware Dispatch Queueをdispatch_busy状態として、いくつかの処理に制限がかかった状態となる。
おわりに
本記事では、リクエストをディスパッチがカーネルスレッドとして起動するところから、I/Oスケジューラからディスパッチする処理の直前となっている次の関数について確認した。
blk_mq_do_dispatch_sched__blk_mq_do_dispatch_schedblk_mq_dispatch_rq_listblk_mq_prep_dispatch_rq
変更履歴
- 2023/11/13: 記事公開
参考
- Block layer introduction part 2: the request layer [LWN.net]
- ブロックレイヤーにおけるリクエストの取り扱い
- blk-mq: introduce BLK_STS_DEV_RESOURCE - Patchwork
- BLK_STS_DEV_RESOURCE 導入パッチ
- [05/11] block: introduce BLK_STS_ZONE_RESOURCE - Patchwork
- BLK_STS_ZONE_RESOURCE 導入パッチ